eSIM vs Physical SIM: Which is better?
The quiet upgrade hiding in your phone
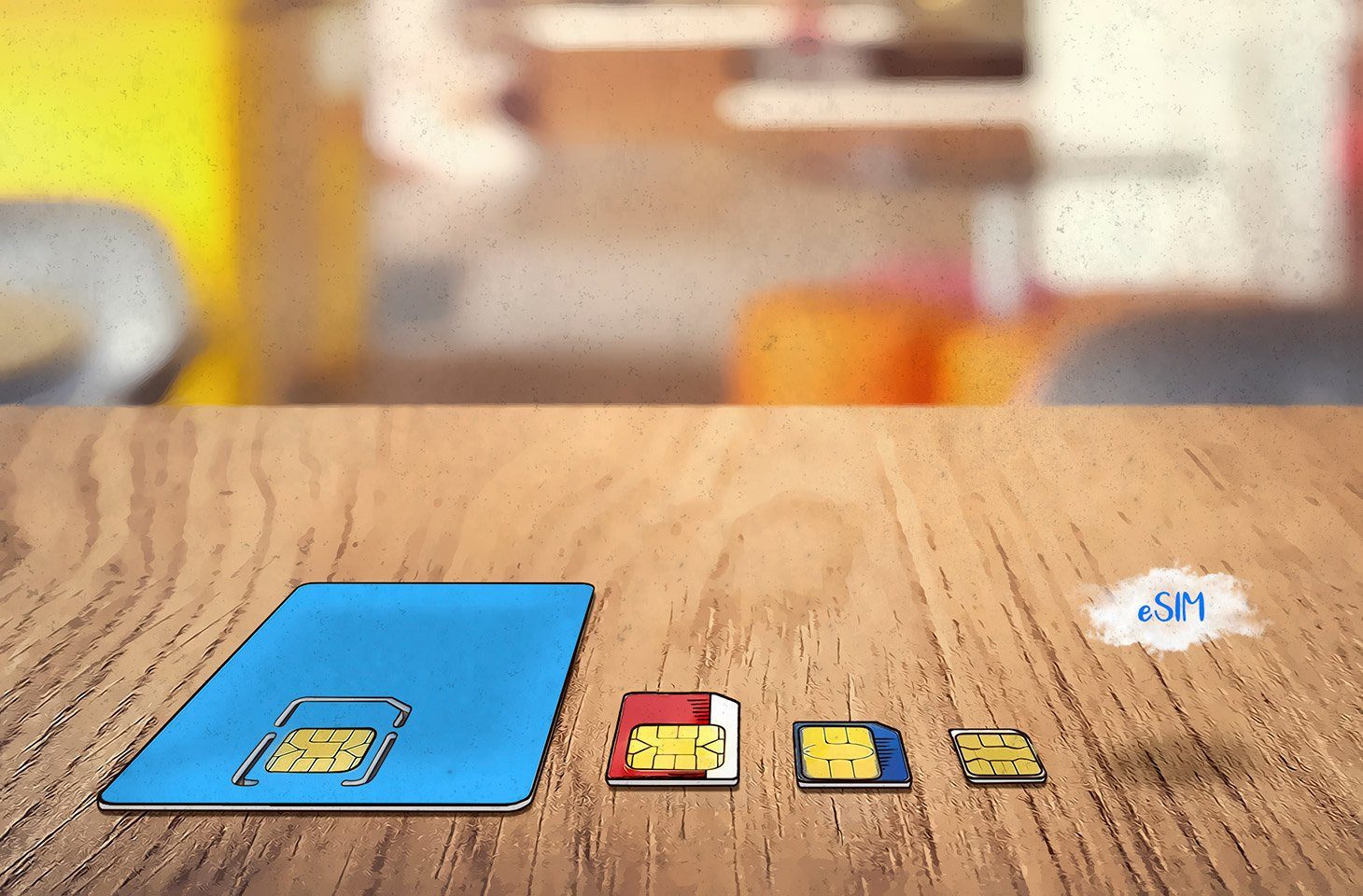

Remember when we used to carry USB drives everywhere and now just send a link instead? SIM cards are on a similar path. For years, a tiny piece of plastic controlled how our phones connected to the world. It worked, so no one questioned it. But as phones became sleeker and more software-driven, swapping chips started to feel outdated.
That shift brought us eSIMs, built in, invisible, and digital by design. In this article, you will see how eSIMs compare to physical SIMs, where they already win, and which one actually fits your life today.
Get 15% off on ByteSim plans with an exclusive TechRadar code
ByteSim offers regional and country plans in over 200 destinations. Features include 5G data, unlimited hotspot, and local phone numbers for some countries. Use code TECHRADAR15 to claim your discount.
TechRadar Pro Approved Sponsored Offer
What is an eSIM and how it works
An eSIM card is a digital version of your physical SIM card and is built into your device’s motherboard instead of being a removable card. It is as simple as activating it remotely with your carrier, and it’s the most flexible and convenient.
Unlike a traditional SIM, an eSIM can store multiple carrier profiles at once and switch between them through your phone’s settings. It uses a technology called Remote SIM Provisioning (RSP), developed by the GSMA, to download and manage network credentials securely over the air. This means you can activate, pause, or delete plans without handling any physical hardware.
eSIMs are compatible with iPhone XS and later, Google Pixel 3+, Samsung Galaxy S20+, and even smartwatches like the Apple Watch or Galaxy Watch.
eSIM vs Physical SIM: Quick comparison
Feature | eSIM | Physical SIM |
Activation | Activates instantly through a QR code or carrier app. No store visit required. | Requires inserting a card and completing a manual activation process. |
Device space | Built into the phone’s hardware, freeing internal space for better design and performance. | Needs a SIM tray and slot, limiting design flexibility. |
Security | Encrypted and linked to the device’s IMEI, making it difficult to clone or remove. | It can be stolen, duplicated, or swapped without the user’s knowledge. |
Carrier switching | Change carriers or plans digitally within minutes through device settings. | Requires a new SIM card and often a trip to a store or service center. |
Durability | Immune to bending, corrosion, or loss because it’s embedded in the device. | Prone to physical damage, wear, or misplacement during swaps. |
Environmental impact | Entirely digital, eliminating plastic cards and packaging waste. | Relies on plastic manufacturing and physical distribution. |
Multi-profile support | Can hold multiple carrier profiles for work, travel, or data-only plans. | Limited to one network profile per card. |
Availability | Supported by most flagship devices and expanding across global carriers. | Universally available but gradually being replaced in newer models. |
Best for | Travelers, professionals, and connected devices like wearables or IoT systems. | Users with legacy phones or in regions without eSIM support. |
10 reasons why eSIMs are better than physical SIMs
1. Instant Activation: No Store Visits Needed
Setting up mobile service no longer requires waiting in line or handling tiny SIM cards. With an eSIM, you scan a QR code or activate through your carrier’s app, and your phone connects within seconds. U.S. carriers such as AT&T, T-Mobile, and Verizon already support instant digital activation through device settings. This frictionless setup defines modern connectivity.
Why it matters: eSIM activation aligns with modern expectations of speed and convenience, allowing you to connect without interruption.
2. Multiple numbers on one device
An eSIM lets you store several carrier profiles on the same phone, making it simple to switch between personal and business numbers or between local and travel lines. The iPhone 15 and Pixel 8 can run two active eSIMs simultaneously, while devices like the Samsung Galaxy S23 support multiple stored profiles. This flexibility turns one device into a global communications hub.
Why it matters: eSIMs enable smarter multitasking and simplify connectivity management for global users.
3. No risk of damage or loss
Traditional SIM cards can bend, break, or get misplaced during swaps. eSIMs are built directly into your device’s motherboard, removing those risks entirely. If your phone is lost or stolen, your carrier can instantly deactivate the digital profile to protect your number and data. This embedded design increases reliability and makes accidental SIM failure virtually impossible.
Why it matters: eSIMs deliver higher reliability and enterprise-grade security for long-term use.
4. Simplified international roaming
eSIMs eliminate the hunt for local SIM cards at the airport. Before you fly, you can purchase regional data plans from providers such as Airalo, Nomad, or ByteSim and activate them upon landing.
These eSIM companies offer affordable roaming in over 190 countries, often at rates up to 80% lower than standard carrier roaming fees.
Why it matters: eSIMs save travelers time and money while ensuring smooth global connectivity.
5. Eco-friendly and sustainable
The world produces more than 4.5 billion SIM cards each year, generating roughly 20,000 tons of plastic waste along with manufacturing and shipping emissions.
eSIMs eliminate this footprint because everything happens digitally. By removing plastic cards and packaging, eSIM adoption directly supports sustainability goals across the telecom sector.
Why it matters: eSIM adoption supports a sustainable, low-impact mobile ecosystem.
6. Enhanced security and anti-theft protection
Unlike removable SIMs, eSIMs are locked to your phone’s IMEI number and protected with GSMA-certified encryption, making them nearly impossible to clone.
Carriers can remotely disable or wipe an eSIM profile if the device is compromised. This security framework has proven to reduce SIM-swap fraud significantly in markets where eSIM use has expanded.
Why it matters: eSIMs raise the standard of mobile security in an era of growing cyber threats.
7. Smooth carrier switching
Switching networks used to involve paperwork and new SIM cards. With eSIMs, you can change carriers or plans directly through settings in a few minutes. U.S. carriers are adopting eSIM-based number portability, letting you compare plans without visiting stores. This instant switching empowers consumers and encourages fair competition.
Why it matters: eSIMs empower users with full control over their network choices
8. Space-saving hardware for better device design
Removing the SIM tray frees internal space for larger batteries, improved cooling, and better cameras. For ultra-compact devices like smartwatches and wearables, that space is essential.
Products such as the Apple Watch, iPad Pro, and Samsung Galaxy Watch 6 already rely exclusively on eSIM technology. The result is a sleeker, more efficient device engineering.
Why it matters: eSIMs help drive the evolution of sleeker, more powerful device engineering.

9. Powers the Internet of Things (IoT)
From connected cars to smart sensors, eSIMs enable IoT devices to stay online without manual setup. They allow remote provisioning at scale, which is crucial for logistics fleets, smart cities, and connected homes.
Companies such as Tesla, Garmin, and Bosch use eSIMs to maintain global connectivity across regions. This is the backbone of always-on infrastructure.
Why it matters: eSIMs are the foundation of a truly connected world.
10. Designed for digital nomads: stay connected wherever you work
For professionals who travel or work remotely, eSIMs provide uninterrupted service across borders. You can keep a home number and add local data plans in minutes through apps like Ubigi or Saily. These services cover over 180 countries and integrate directly into phone settings. eSIMs make borderless work and travel truly practical.
Why it matters: eSIMs offer continuous, borderless connectivity for the modern global workforce.

The limitations of eSIMs you should know
eSIMs are the future, though physical SIMs will linger for older devices and developing markets. Here’s what to keep in mind before you make the switch:
- Limited device support: Some older or budget smartphones still don’t include eSIM hardware. Always check compatibility before purchasing a new device.
- Carrier gaps: Not every mobile carrier offers full eSIM functionality, especially for prepaid plans or in developing markets.
- Transfer challenges: Moving an eSIM between phones can sometimes be tricky, particularly with networks like AT&T. Fortunately, brands like Apple and Google are improving this with smoother transfer tools.
- Adoption lag: While the industry is moving fast, it’ll take a few more years for eSIMs to fully replace physical SIMs everywhere.
Global adoption and the future: Are physical SIM cards going away?
The shift is no longer hypothetical. It is already underway. In the United States, Apple began the transition when the iPhone 14 launched without a SIM tray, a move that clearly signaled the beginning of the end for the physical SIM era. In Apple's latest release, we saw the iPhone Air erasing the physical SIM card tray.
Globally, the transformation is gaining momentum. According to GSMA Intelligence, eSIM smartphone connections are expected to reach 850 million by 2025 and rise to 6.7 billion, or roughly 76% of smartphones, by 2030.
Several reasons are pushing this change:
- Design efficiency: Devices such as smartwatches, connected cars, and IoT systems are eliminating SIM trays to save space and improve durability.
- Network readiness: More than 260 operators have already launched commercial eSIM services, and standards such as SGP.32 for remote provisioning are fully established.
Still, many regions will continue to rely on SIM cards for legacy devices, prepaid plans, and slower carrier rollouts.
However, the trend is pretty clear now. For new flagship devices and connected ecosystems, the SIM slot is quickly becoming a thing of the past.
Takeaway: If your next phone arrives without a SIM tray, that is intentional. The industry is moving toward fully digital connectivity, and the plastic card that powered mobile networks for three decades is beginning to fade into history.
What is the difference between an eSIM and a regular SIM card?
The difference between an eSIM and a regular SIM card lies in how they connect you to a network. An eSIM is built directly into your device and activated digitally through your carrier, while a regular SIM is a removable plastic chip. eSIMs enable instant setup, remote provisioning, and eliminate the need for physical swapping.
Which is better: eSIM or physical SIM?
eSIMs are better than physical SIMs for speed, flexibility, and sustainability. They let you activate service instantly, store multiple carrier profiles, and reduce plastic waste.
Physical SIMs still work universally, but eSIMs are rapidly becoming the global standard, especially as Apple and Samsung move toward eSIM-only flagships.
Can I use eSIM and a physical SIM together?
You can use an eSIM and a physical SIM together on most modern smartphones. This setup is ideal for people who manage separate work and personal numbers or travel frequently. Devices like the iPhone 15 and Samsung Galaxy S23 allow both profiles to run simultaneously for seamless dual connectivity.
Is eSIM safe and secure?
eSIM is more secure than a physical SIM because it’s encrypted, tied to your device’s IMEI, and can’t be physically removed or cloned. Carriers can remotely lock or erase an eSIM if your phone is lost, preventing SIM-swap fraud and unauthorized access, a major upgrade in mobile security.
How do I activate an eSIM?
To activate an eSIM in the U.S., scan the QR code provided by your carrier or download your plan directly through their app. Major carriers like AT&T, Verizon, and T-Mobile support instant activation in iOS and Android settings, no store visit needed. Most newer phones can be activated in under a minute using eSIM Quick Transfer or carrier-branded apps.
Is eSIM available in my country?
eSIM is fully available across the United States, supported by all major networks, Verizon, AT&T, T-Mobile, and regional carriers like UScellular. Every flagship phone released in recent years, including the iPhone 14 and Pixel 8, supports eSIM-only or dual-eSIM configurations. Travelers can also buy data-only eSIMs from providers such as Airalo or Ubigi for short-term U.S. connectivity.
What phones support eSIM?
Phones that support eSIM include all iPhones from XS onward, Google Pixel 3 and newer, and Samsung Galaxy S20 series and later. High-end Huawei, Oppo, and Motorola models also feature built-in eSIMs. Beyond phones, many tablets, laptops, and wearables like the Apple Watch Series 9 use eSIM too.
Can I transfer an eSIM between phones?
You can transfer an eSIM between phones, though the process depends on your carrier and device. Apple’s Quick Transfer allows instant migration between iPhones, while other networks provide a new QR code for reactivation. Most carriers are streamlining this process to make switching devices effortless.
Sign up to the TechRadar Pro newsletter to get all the top news, opinion, features and guidance your business needs to succeed!
Pawan Singh is a tech writer at TechRadar Pro, where he contributes fresh how-to guides, product reviews, and buying guides within the tech industry. Apart from his writing duties, Pawan offers editorial assistance across various projects, ensuring content clarity and impact. Outside the world of tech, he enjoys playing basketball and going on solo trips.


